Welding is a critical process in various industries, from construction to manufacturing, and the choice of welding materials plays a pivotal role in determining the quality and durability of the final product. Selecting the appropriate welding materials can significantly influence the effectiveness, strength, and longevity of welded joints. Different applications require specific types of welding materials to ensure optimal performance under varying conditions, such as temperature, corrosion, and mechanical stress.
This guide explores the best welding materials suited for various applications, highlighting the importance of compatibility between the materials being welded and the filler used. Whether working with metals, plastics, or composites, understanding the characteristics and behaviors of different welding materials can lead to more successful outcomes in fabrication projects. By delving into the properties and uses of various welding materials, we aim to equip professionals with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions tailored to their specific requirements.

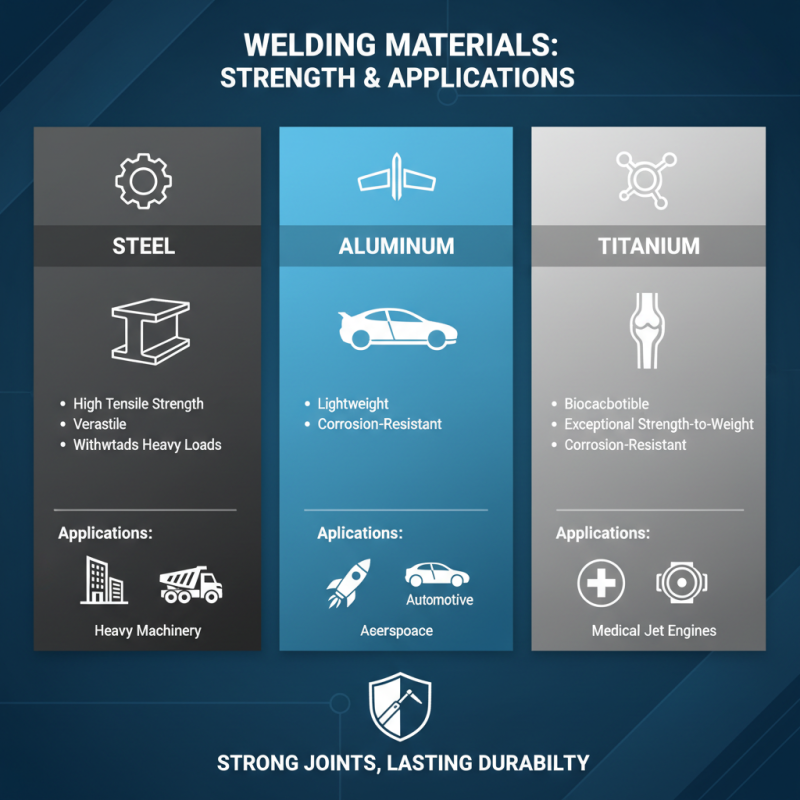
When it comes to welding, selecting the right materials is crucial for achieving strong and durable joints. Common welding materials include steel, aluminum, and titanium, each with distinct properties that make them suitable for specific applications. Steel, for instance, is widely used due to its high tensile strength and versatility. It can withstand heavy loads, making it ideal for construction and heavy machinery. On the other hand, aluminum is favored for its lightweight and corrosion-resistant characteristics, proving essential in the automotive and aerospace industries.
Tips: When choosing welding materials, always consider the environment in which the welded item will be used. For instance, if you require a lightweight yet strong solution, aluminum or its alloys may be preferable. Conversely, for structures subjected to high stress or heavy weights, ensure to opt for a high-grade steel.
Another commonly used material is titanium, known for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and resistance to high temperatures. This makes it ideal for applications in the medical field and aerospace, where both reliability and lightness are paramount. Understanding these materials allows welders to make informed decisions, ensuring safety and performance in their projects.
Tips: Familiarize yourself with the melting points and compatibility of different welding materials. This knowledge can prevent mixing incompatible materials that can lead to weakened joints and potential failures in critical applications.
When it comes to welding materials for steel applications, several factors play a crucial role in determining the best options. The primary materials include various types of steel electrodes, filler metals, and welding wires, each catering to specific requirements based on the application. For instance, mild steel is often welded with E7018 electrodes, known for their excellent mechanical properties and ease of use. In contrast, high-strength steel applications may necessitate the use of filler materials that can handle elevated stress and provide optimal joint strength, such as E11018 or other alloyed electrodes.
Additionally, the welding process itself influences material selection. For MIG welding of steel, ER70S-6 filler wire is frequently chosen due to its versatility and ability to produce clean, strong welds. In more demanding environments, where corrosion resistance or toughness is paramount, stainless steel filler rods or flux-cored wires can be employed for enhanced performance. Understanding the specific requirements of the project, including the type of steel being welded and the service conditions, allows welders to make informed decisions about the best welding materials to ensure durable, high-quality results.
When welding aluminum and its alloys, selecting the appropriate welding materials is crucial for achieving strong and lasting joints. The most commonly used fillers for aluminum welding are 4047 and 5356. The 4047 alloy is preferred for its excellent fluidity and low shrinkage, making it suitable for intricate welds and when working with heat-treated aluminum alloys. It is often favored for automotive and aerospace applications where precision is paramount. In contrast, 5356 filler is known for its high strength and good corrosion resistance, making it ideal for marine environments and structural applications.
Choosing the right welding electrode is equally important. For MIG welding, the ER4047 and ER5356 wires are standard options that complement their respective filler materials. Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) welding, another popular method for aluminum, often utilizes 4047 or 5356 rods, depending on the desired properties of the finished weld. Using the correct shielding gas, such as pure argon or a mixture of argon and helium, further enhances the quality of the weld. By selecting the optimal materials and processes, welders can ensure strong bonds in various applications, from light fabrication to heavy-duty industrial use.
| Application | Welding Material | Suitable Aluminum Alloy | Welding Process | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Automotive | 4047 Alloy Fill Rod | 6061, 6063 | TIG, MIG | Good for high strength |
| Aerospace | 5356 Alloy Wire | 5052, 5083 | MIG | Corrosion-resistant |
| Marine | 4047 Alloy | 5086, 5083 | TIG, MIG | Excellent in salt water |
| Construction | 6061 Alloy Wire | 6061 | MIG | Good weldability and strength |
| Food Industry | 4045 Alloy Tubing | 3003, 5052 | TIG | Clean and non-toxic |
When selecting welding materials for stainless steel, several key considerations must be taken into account to ensure optimal results. First and foremost, the type of stainless steel being welded plays a crucial role in material selection. Different grades of stainless steel, such as austenitic, ferritic, and martensitic, have varying chemical compositions and properties that can affect the choice of filler materials and welding techniques. Understanding these differences is essential for maintaining the integrity and strength of the final weld.
Another important factor is the welding method chosen for the specific application. Techniques such as TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) or MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding each have their advantages and limitations when working with stainless steel. For instance, TIG welding is often preferred for its precision and control, making it ideal for thinner sections and detailed work. On the other hand, MIG welding tends to be faster and more efficient for thicker materials, but requires careful management of heat input to minimize distortion and maintain corrosion resistance. Ultimately, selecting the right welding materials and techniques hinges on a thorough understanding of the project requirements and the properties of the materials involved.
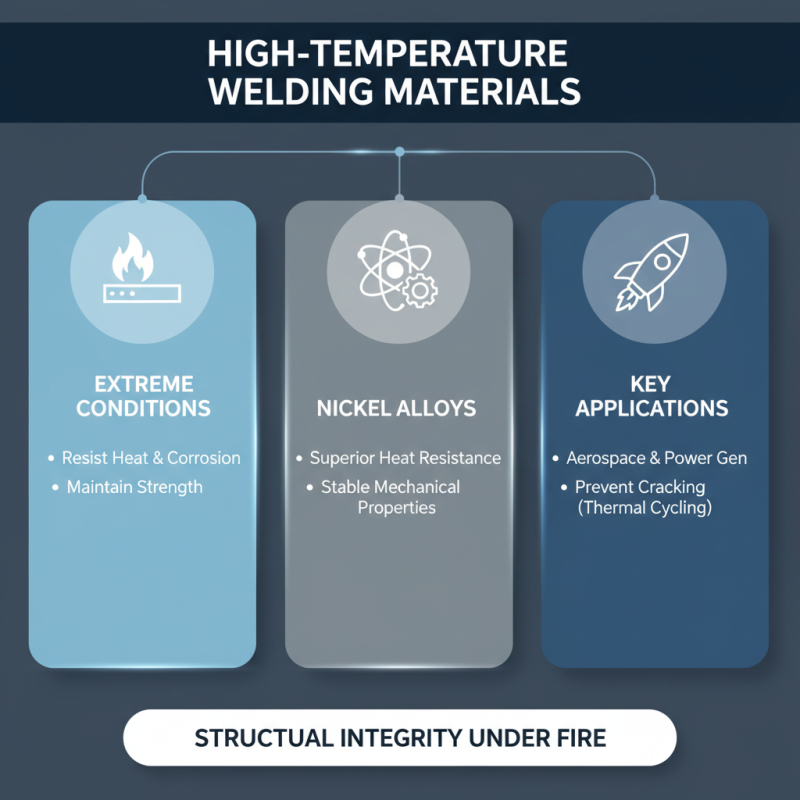
High-temperature applications in welding necessitate materials that can withstand extreme conditions without compromising structural integrity. Commonly used welding materials for these applications include nickel alloys, which offer exceptional resistance to heat and corrosion. These alloys maintain their mechanical properties even at elevated temperatures, making them suitable for industries like aerospace and power generation. Their ability to endure thermal expansion and contraction is vital in reducing the risk of cracking during the welding process.
Additionally, ceramic materials are often employed in high-temperature welding due to their ability to withstand intense heat and thermal shock. They provide a unique advantage in applications that require welding of dissimilar metals, where thermal compatibility is crucial. The use of specialized fluxes and shielding gases is also essential in these circumstances to protect the weld pool from oxidation and contamination, ensuring a strong and durable joint. By carefully selecting the right materials and techniques, fabricators can achieve reliable results that meet the demanding standards of high-temperature applications.





Contact Us
Pemamek Ltd